Doctor burnout is a significant problem impacting the quality and schedule of health care in the United States. The increasing rate of this issue stimulated a current research study targeted at recognizing its roots. The research study was released online in JAMA Network Open
Intro
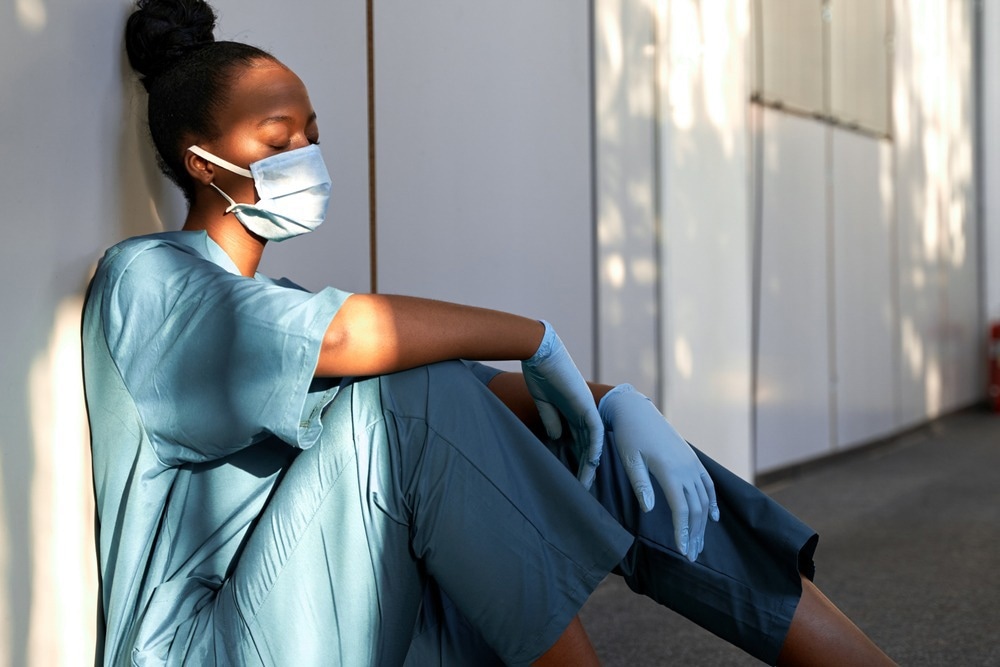
Doctor burnout describes “ a state of psychological, physical, and psychological fatigue brought on by extended tension in the work environment” Several elements might cause burnout, consisting of absence of self-reliance at the work environment, overwork, and absence of time for non-professional activities.
The significance of burnout in the medical field depends on the capacity for mistakes in medical diagnosis and treatment, the lower client fulfillment rating, and the increased chances of absence. It might cause less doctors being readily available for health care, which might affect the neediest locations and the most sought-after specializeds initially.
This might trigger client waiting times for consults to increase, reducing access to health care and minimizing the quality of care also.
The Maslach Burnout Stock (MBI) was utilized to evaluate doctor burnout. The MBI steps doctor burnout utilizing 3 subscales, specifically, Fatigue, Cynicism, and Specialist Effectiveness
Remarkably, over 45% of doctors reported several burnout signs utilizing this scale. Some scientists reported a high increase in burnout rates with the beginning of the coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, specifically as the 2nd year ran its course.
The significant functions observed amongst doctors at this time were depersonalization and psychological fatigue. Given that numerous factors might add to predisposition in the estimate of the nationwide burnout rate amongst doctors, the present research study looked for to make up for these elements and attain a more precise figure.
A few of these confounding elements consist of the truth that doctors with more experience tend to feel less stressed out; those with more burnout tend to leave the medical field. Additionally, the action rate in burnout studies is typically low. The present research study utilized a high-response study, connecting reactions by individuals through all 3 studies to conquer sources of predisposition.
What did the research study program?
The research study consisted of 3 studies covering nearly 1400 doctors coming from the Massachusetts General Physicians Company (MGPO). This number represents 73% of the number who initially registered in the very first study. The participants came from either sex in equivalent percentages, however a little over two-thirds were White. About 13% were Hispanic.
All 3 studies had a high action rate, connected to the substantial monetary reward of $850. While the very first and 2nd studies in 2017 and 2019 acquired a 93% action rate each, the last one in 2021 had a 92% action.
The study took a look at 4 locations: profession and settlement fulfillment, wellness, administrative work, and management and variety material. If 2 of the 3 MBI subscales revealed a high rating, burnout was identified to be present; otherwise, it was missing. Nevertheless, a different analysis likewise took a look at the steps in a constant style.
Over the 3 studies, more than one in 4 doctors were stressed out, without any modification observed in the state of burnout. Likewise, more than one in 3 doctors did not experience burnout at any phase.
To put it simply, more than 60% did not alter their burnout rating over the 3 studies, however over 30% revealed a boost in their currently high ratings.
Over a 3rd of the doctors had actually remained in practice for 11-20 years, showing substantial experience. In this group, the rate of burnout decreased a little from about 44% in 2017 to 42% in 2019. Nevertheless, it then soared to 50% in 2021. Compared to less skilled doctors, the chances of burnout in those in practice for 30 or more years were just a fifth of those with less than a years of experience.
The entire associate revealed the very same pattern, with the burnout threat doubling in 2021, whereas it stayed steady over the 2 previous studies. Females in this field were at 50% greater threat for burnout than males. Once again, those operating in medical care were nearly 3 times most likely to stress out than doctors in internal medication.
The researchers likewise discovered that private variation is significant in figuring out burnout. Throughout the very same research study duration, for example, over 60% of doctors reported fatigue at the very same level in all studies, whether high or low. This held true for all 3 subscales.
Physicians with less burnout invested less time on non-physician (administrative) jobs, listed below a quarter of their time vs over 30% in the group with high burnout. They were more pleased with their task and reimbursement and had actually worked for more years. Maybe it requires time to reach a level of practice where fulfillment surpasses the tension.
What are the ramifications?
The increasing burnout rate amongst United States doctors is a sound issue, offered the increasing rates of persistent health conditions needing specialized and long-lasting health care. “This pattern represents a possible danger to the capability of the United States healthcare system to look after clients and requires immediate options.”